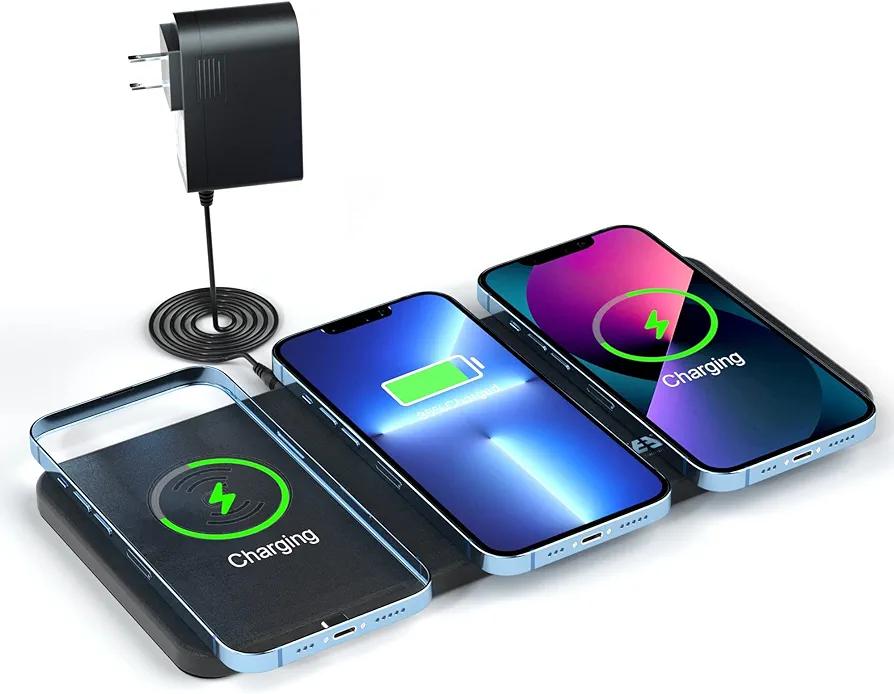
In our modern lifestyle, there’s a constant dependence on electronic devices that are power-hungry. From smartphones and smartwatches to laptops and earbuds, we are always in need of a charge. Enter Qi charging, a revolutionary wireless technology that offers solutions to those awkward charging cables and misplaced adopters. But how exactly does it work, and how can we use it to its full potential?
This comprehensive guide will demystify the science behind it, explore its benefits, delve into its drawbacks, and guide you on how to use it proficiently. As we navigate this burgeoning technological advancement, allow us first to familiarize ourselves with Qi charging’s fundamental principles.
What is Qi Wireless Charging?

Qi (pronounced “chee”) is a global standard for wireless power and charging. Developed by the Wireless Power Consortium, it enables power transfer over distances of up to 4 cm, making it incredibly practical for everyday use. It operates using inductive charging, wherein power is sent through coils to a device via a magnetic field.
What makes Qi wireless charging unique is that it allows for devices from different manufacturers to be compatible with the same charging station. This has tremendous implications for the convenience and ubiquity of wireless charging. Here are some key points to understand:
- Compatible Devices: Any device that supports Qi wireless charging, whether it’s a smartphone, tablet, or wearable, can be charged using a Qi-enabled cradle or pad. There’s no need for a separate charging station for every single device.
- Reduced Clutter: As you don’t need multiple chargers and cables, Qi wireless charging can effectively reduce clutter in your work or living space.
- Universal Access: Many public venues, such as airports, hotels, and coffee shops, are starting to offer Qi-enabled charging stations, making charging on the go much easier.
The heart of Qi wireless charging lies in its inductive coils. A Qi charger has a transmitter coil, and the device being charged has a corresponding receiver coil. The transmitter coil creates a magnetic field which induces a current in the receiver coil, thereby charging the device. Here’s a simple illustration:
| Qi Charger | Device |
| Transmitter coil | Receiver coil |
In a nutshell, Qi wireless charging represents a giant stride towards a world untethered from wired charging, where the only thing you need is a Qi-enabled surface to power up your devices.
The Science and Engineering Behind Qi Power Transmission
As we delve into the world of Qi wireless charging, one can’t help but marvel at the brilliant science and engineering involved in this technology. The underlying principle of Qi power transmission lies in the physics of electromagnetic fields at resonance, which allows energy to be transferred over a short distance.
Resonant Inductive Coupling: The charging base has a transmitter coil and the device to be charged has a receiver coil. When an alternating current is passed through the transmitter coil, it generates an oscillating magnetic field which induces an alternating current in the receiver coil. This current is then converted into direct current to charge the battery. To maximize efficiency, the transmitter and receiver must be tuned to the same frequency.
| Transmitter Coil | Generates an oscillating magnetic field |
| Receiver Coil | Induces an alternating current |
The engineering behind the Qi system incorporates various safety measures to ensure devices are charged efficiently and safely. One such feature is the ‘Foreign Object Detection (FOD)’ which can detect and block power transfer when a foreign object is found within the inductive coupling area. In addition, Qi charging also regulates the power consumption, ensuring that the device only draws the power it needs. This is achieved through an ongoing communication process between the charging pad and the device.
- Foreign Object Detection (FOD): It prevents power transfer when a foreign object is found within the inductive coupling area.
- Power Regulation: Qi charging regulates power consumption by responding to ongoing communication between the charging pad and the device.
| Feature | Function |
| Foreign Object Detection | Prevents power transfer when a foreign object is found |
| Power Regulation | Regulates power consumption on the device |
Pros and Cons of Switching to Qi Wireless Charging Technology
 The Qi wireless charging technology has become increasingly popular among smartphone users all over the world. However, just like any other technology, it has its significant benefits and unavoidable disadvantages that consumers should weigh up.
The Qi wireless charging technology has become increasingly popular among smartphone users all over the world. However, just like any other technology, it has its significant benefits and unavoidable disadvantages that consumers should weigh up.
The pros are quite enticing. Firstly, the convenience factor is undoubtedly off the charts. With Qi wireless charging, you no longer need to fumble with cords or struggle to find a port. Your device only needs to be placed on the charging pad. Secondly, the technology presents a cleaner and more organized charging solution. Clear your workspace or bedside table of pesky cords and enjoy a more modern and minimalist look. Lastly, the standardization of Qi technology means that one charging pad can power up a range of devices, from your smartphone to your smartwatch.