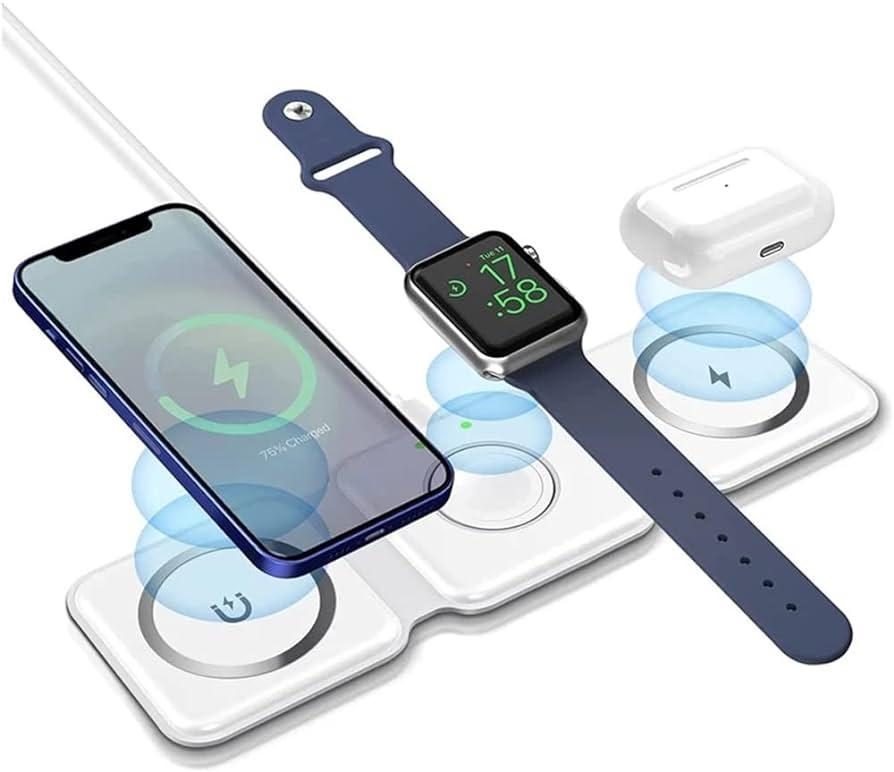
As we continue to embrace technology’s pervasive presence in our daily lives, many of us have become familiar with the convenience of wireless charging for our devices. Yet, despite its rising popularity, the science behind this innovation still remains a mystery to most. This article seeks to demystify this technology. From its underlying principles to its intricate operation, we’ll explore the remarkable processes that enable you to power up your smartphone, tablet, or smartwatch without the need for plugging in. Join us as we delve into understanding the technology behind wireless charging.
Understanding the Basics of Wireless Charging Technology

Wireless charging, often called inductive charging, uses the principles of electromagnetism to produce an electrical charge over a distance. Fundamentally, it utilizes an energy transfer between two objects through electromagnetic fields. This fascinating technology comprises of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter is the actual wireless charger or charging station. The receiver, on the other hand, is built into the device being charged.
The wireless charging technology operates by following a basic three-step process. Firstly, the source (transmitter) generates an alternating electromagnetic field with the assistance of an internal induction coil. Thereafter, this generated electromagnetic field propagatively transfers energy over a distance to the receiver located in the portable device. Finally, the received energy is converted back into electric current and is used to charge the device. Consequently, this sees to the charging of your device without being physically connected to a charger. It’s indeed a simple yet ingenious solution in the world of technology.
The Primary Components of Wireless Charging Technology
In reality, the beauty of this technology lies within its components. Understanding how they function together can give one a clearer picture of how wireless charging operates. The prime components include:
- Induction Coils: These act as the main power transformers, enabling the transfer of power between two objects.
- Electromagnetic field: Generated by the induction coils, it serves as the medium through which energy is passed.
- Capacitor: This electronic component accumulates and stores the electrical energy generated.
- Rectifier: It converts the received alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) for charging the device.
Let’s explain their roles a bit succinctly in the following table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Induction Coils | Enable power transfer between two objects |
| Electromagnetic Field | Serves as transfer medium for energy |
| Capacitor | Accumulates and stores electrical energy |
| Rectifier | Converts AC into DC for charging the device |
Unveiling the Science Behind Wireless Power Transfer
The world of technology is continuously evolving and one development that’s making a significant impact is wireless power transfer, with wireless charging leading the way. To start with, it’s crucial to grasp the core concept which is magnetic resonance or magnetic induction. This is a principle that has existed since the time of Nikola Tesla, a visionary scientist who dreamt of delivering power wirelessly. Magnetic induction occurs when an electrical current flowing through one wire induces a current in another wire without direct contact.
At the heart of a wireless charger are two coils, a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter coil is in the charging station while the receiver is in the device being charged. When electricity runs through the transmitter coil, it generates a magnetic field which extends to the receiver coil when they are close enough. This magnetic field induces a current in the receiver coil, thus charging the device.
- Transmitter Coil:This is the coil in the charging base or station. It is connected to a power source and creates a magnetic field when electricity is passed through it.
- Receiver Coil:Found in the device that needs to be charged, it ‘receives’ the magnetic field created by the transmitter coil and converts it into electricity to charge the device’s battery.
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Transmitter Coil | Creates a magnetic field when energized. |
| Receiver Coil | Induces a current from the generated magnetic field. |
Notably, the efficiency of this transfer depends on the distance between the two coils, the alignment, and the coil quality. The adoption of this technology has resulted in a world teeming with wirelessly charged electronic devices, from smartphones to electric toothbrushes, minimizing the need for cumbersome wiring and offering a simple and efficient charging solution.
Comparing Various Types of Wireless Charging Techniques
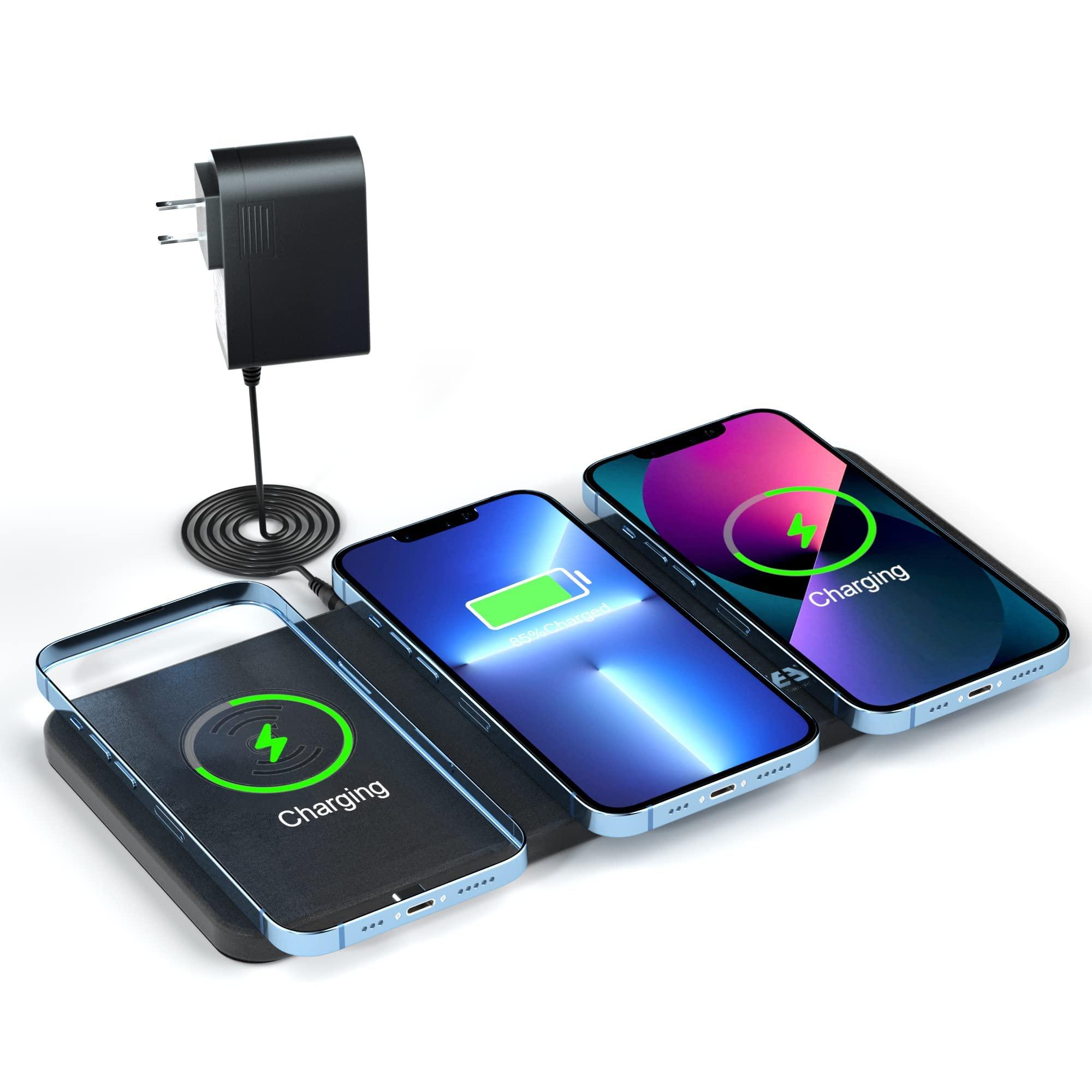

Wireless charging technology has evolved over the years, resulting in some innovative charging methods that increase user convenience. The three key types include Inductive Charging, Resonant Charging, and Radio Frequency (RF) Charging.
Inductive Charging is a popular method where energy is transferred between coils in close proximity. Here, an integral component is a charging pad that requires a direct physical contact with the device. Products like Android’s Qi Wireless Charging and Apple’s AirPower are examples of Inductive Charging. On the other hand, Resonant Charging works on the same principal but allows for longer distance charging, through the efficiency of magnetic resonance. This method is often seen in electric toothbrush chargers or in more large-scale applications like electric vehicle charging stations. Lastly, Radio Frequency (RF) Charging utilizes RF waves to transmit power over longer distances and through various obstacles. It’s considered the future of wireless charging, being potentially incorporated into WiFi signals to charge devices.
| Type of Charging | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Inductive Charging | Efficient power transfer, universal standard across major brands | Requires close proximity or direct contact |
| Resonant Charging | Enables longer distance charging, practical for larger devices | Lower efficiency, can be expensive to implement |
| Radio Frequency Charging | Enables charging through obstacles and over long distances | Still in developmental stage, can interfere with other signals |
Revolutions in wireless charging technology is likely to continue shaping our digital civilization. With in-depth knowledge of these methods, consumers and manufacturers alike can make informed decisions to effectively harness the benefits of wireless charging.
Maximizing the Efficiency of Your Wireless Charging Device

Wireless charging unitizes the phenomenon of electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between two objects. The core technology utilizes two types of coils: a transmitter coil in the charging unit and a receiver coil in the device to be charged. An AC voltage is applied to the transmitter coil in the charging station, which generates a magnetic field and causes a current to flow in the receiver coil, thus charging the device wirelessly.
To maximize the efficiency of your wireless charging device, it’s crucial to understand and utilize some key strategies. Most importantly, direct coil alignment plays a major role in optimizing wireless charging. This ensures that the device and the charger are properly synced for optimal energy transfer. Next, ensure you’re using a high-quality charging unit that matches the power requirements of your device. Utilize chargers made by reliable and respected manufacturers, as they adhere to strict safety and performance standards. Also, free your device from bulky cases or covers that could obstruct the electromagnetic field.
- Direct Coil Alignment: Align the coils properly to improve efficiency.
- High-Quality Charging Unit: Invest in a quality charger to ensure safety and performance standards are met.
- Remove Obstructive Cases: Bulky cases or covers could hinder the charging process, always remove them while charging.
| Technique | Goal |
|---|---|
| Direct Coil Alignment | Improve efficiency |
| High-Quality Charging Unit | Ensure safety and performance standards |
| Remove Obstructive Cases | Hinder interference |
In conclusion, these small adjustments can significantly improve the efficiency of your wireless charging device. Thus, enhancing your overall user experience and extending the lifespan of your device.
How to Choose the Best Wireless Charging Technologies

Wireless charging technology has revolutionized the way we power our devices. Easily eliminating the chaotic mess of charging cables for various devices, it has become a popular choice among many users. When selecting these technologies, consider a couple of things such as their charging speed and compatibility. Charging speed is determined by power output. Most wireless chargers come with standard output power but the higher output models are able to charge devices faster. Compatibility on the other hand, suggests that not all wireless charging technologies may work with your device. Ensuring that the technology you choose is compatible with your device is crucial to reap the benefits.
| Charging Speed | Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Standard and High Output models | Depends on the device |
Also, scrutinize the warranty and price while purchasing. Most charging technologies offer at least a 1-year warranty but it’s always safer to go for those that offer more. Regarding prices, they generally vary with the brand and functionality.
- Warranty: Most companies offer a 1-year warranty, can go up to 2-3 years.
- Price: Varies depending on brand and functionality, can range from $10 to a few hundred.
Make your decision not just based on what you see, but also by considering its functionality and your usage. Picking the right wireless charging technology ensures a seamless, hassle-free charging experience.
Undertaking the Safety Measures for Wireless Charging
Additionally, it’s crucial to use appropriately designed and certified charging pads from trusted manufacturers. Counterfeit or poorly made chargers can pose real safety threats. Protection features such as Foreign Object Detection (FOD) play a significant role in improving safety by automatically detecting and avoiding power transfer to unintended objects, such as coins or keys, which may end up on the charging pad. Here is a quick overview of the safety measures you need to consider:
- Regulatory compliance: Ensure the wireless charger conforms to safety standards such as FCC or CE.
- Heat control: Look for chargers with thermal management to prevent overheating.
- Overcharge prevention: Smart chargers stop transferring power when your device is fully charged.
- Use of high-quality charging pads: Counterfeit or poorly made chargers can be dangerous.
- Foreign Object Detection (FOD): This feature prevents power transfer to unintended objects.
The Future of Wireless Charging: What to Expect
Wireless charging has become a pivotal part of our everyday lives, with more devices incorporating this convenient feature. This technology utilizes the principle of electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between two objects. The base station, or charging pad, generates a magnetic field which interacts with the mobile device to create a current that charges the battery.
It is anticipated that future advancements in wireless charging technology will focus on increasing charging range and improving efficiency. Imagine a future where your electronic devices can be charged by simply being in the same room as the charger. Achieving this kind of truly wireless charging will require advances in resonant inductive coupling or the development of completely new technologies.
- Faster Charging Speeds: With sophisticated technology infrastructure, wireless charging will continue to evolve with dramatically increased charging speeds. This could mean a world where the time taken to fully charge devices is significantly reduced.
- Universal Charging Standards: Future wireless charging is also expected to provide universal solutions for all devices. Amid a plethora of devices with different charging needs, a universal charging standard would simplify the process for users.
- Wireless Charging Stations: As wireless charging becomes more commonplace, it’s possible to see more public venues equipped with wireless charging stations. This means you could charge your phone at a restaurant, in a taxi, or at the library without needing a physical charger.
| Current Technology | Potential Future Development |
|---|---|
| Inductive Charging | Resonant Inductive Coupling |
| Limited Range | Extended Range |
| Single Device Charging | Multiple Device Charging |
With these advancements in mind, it’s evident that the future of wireless charging holds immense potential and it’s an exciting time to witness the evolution of this technology.
In Retrospect
In conclusion, wireless charging represents one of the cutting edge technological developments today. Understanding the technology behind it helps us to appreciate it, making use of electromagnetic fields in transferring energy between two objects. Advancements in this field could forever change the way we keep our devices powered, eliminating the need for tiresome cables and plugs. Future prospects include long-range wireless charging and more efficient power transfers. By shining a light on how it works, we’ve taken one step further into appreciating the rich, ever-evolving tapestry of technology that surrounds us every day. Stay tuned for more insights on exciting technological processes and trending topics.